Eruptive events refer to the sudden release of energy, typically in the form of volcanic activity, in the Earth’s crust creating seismic disruptions. These events are characterized by the ejection of lava, ash, and gases from a volcano, leading to potential climate changes, environmental alterations, and in some cases, mass extinctions. The intensity and impact of eruptive events can vary, ranging from localized destruction in the immediate vicinity of the eruption to global climatic effects. For instance, the infamous eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD obliterated the cities of Pompeii and Herculaneum, preserving them under a thick layer of pumice and ash, providing future generations with a stark reminder of nature’s unpredictable fury.
In scientific terms, eruptive events are classified based on the nature of the eruption, the type of magma involved, and the resulting landform. For example, effusive eruptions occur when viscous magma escapes through cracks in the Earth’s crust and slowly flows out onto the surface, creating new landforms such as shield volcanoes. Conversely, explosive eruptions happen when gas-rich magma is ejected violently from a volcano, resulting in the formation of composite or stratovolcanoes.
It is crucial to note that eruptive events are not confined to the terrestrial sphere. They occur across the universe, often on a much grander scale. The Sun, for instance, experiences solar flares – gigantic eruptions that occur near sunspots, releasing vast amounts of energy into space and occasionally disrupting satellite communications on Earth. Similarly, geysers on Saturn’s moon, Enceladus, and the suspected cryovolcanism on Pluto, further demonstrate the universal nature of eruptive events.
Monitoring and predicting eruptive events is a significant focus of geologists, volcanologists, and astrophysicists. They employ an array of sophisticated tools and techniques, from ground-based observations to satellite imagery, to seismic and acoustic data, for early detection of potential eruptions. This information is vital for disaster management planning, enabling authorities to evacuate populations at risk and minimize the impact of such events.
Despite the destructive potential of eruptive events, they play an essential role in shaping the Earth’s landscapes, enriching soils with nutrients, and influencing climate patterns. The ash and lava ejected during volcanic eruptions break down over time, contributing essential minerals to the soil, thereby fostering lush vegetation growth in these regions. Moreover, large-scale eruptions can impact global climate by releasing aerosols into the atmosphere, which reflect sunlight back into space, causing the Earth’s temperature to decrease temporarily, a phenomenon known as volcanic winter.
In conclusion, eruptive events, while potentially devastating, are an integral part of the Earth’s dynamic geological processes and the larger cosmic phenomena. They remind us of the immense power and unpredictability of nature, demonstrating the need for continuous monitoring and scientific understanding. By studying these events, we can not only prepare ourselves better for future occurrences but also enrich our knowledge about the intricate workings of our planet and the universe.
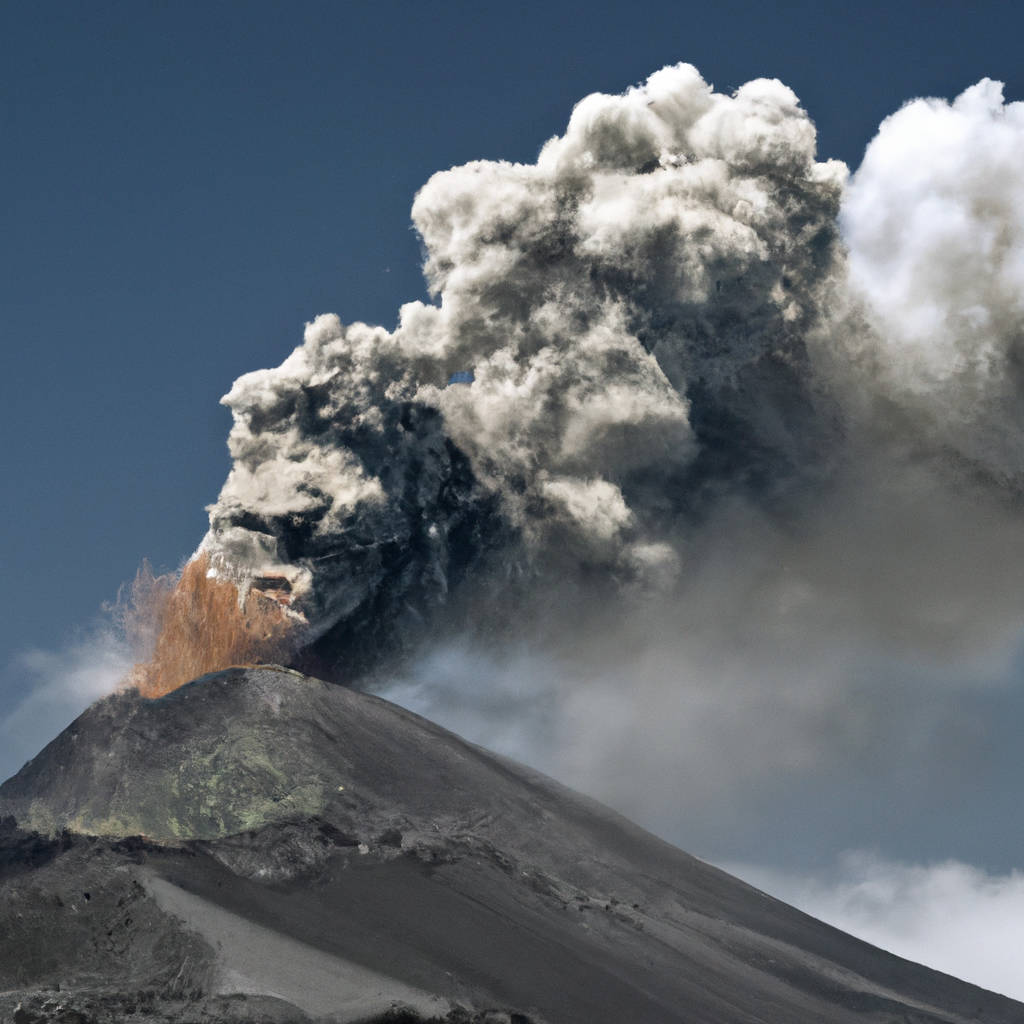

Understanding Volcanic Activity
Volcanic activity is a fascinating and complex natural phenomenon. In essence, it refers to the eruption of molten rock, known as magma, from beneath the Earth’s surface, which is driven by the movement of tectonic plates and the release of gases. Understanding volcanic activity is crucial for numerous reasons. Firstly, it helps us predict future eruptions, which can save lives and minimize property damage. Secondly, it aids in comprehending the Earth’s geological history, giving us insights into the planet’s formation and evolution over billions of years.
Volcanologists, scientists who study volcanoes, utilize a range of techniques to monitor volcanic activity. These include seismology, which detects vibrations in the Earth’s crust, and remote sensing, where satellites capture images and data from space. Additionally, they may collect physical samples such as rocks and gases for laboratory analysis.
Understanding volcanic activity also has broader implications for understanding the Earth’s climate. Volcanic eruptions can have significant impacts on the planet’s weather patterns, primarily through the release of aerosols and sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere, which can reflect sunlight away from the Earth and cause global cooling.
Moreover, volcanic activity contributes to the Earth’s carbon cycle. Volcanoes release large amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, which is a critical part of life on Earth. However, increased volcanic activity could also contribute to climate change due to the excess release of greenhouse gases.
In the realm of planetary science, studying volcanic activity extends beyond Earth. For instance, understanding the volcanoes on Mars or Jupiter’s moon Io can provide valuable insights into their geological history and potential for extraterrestrial life.
In conclusion, understanding volcanic activity is not just about comprehending the dynamics of fiery, molten eruptions. It’s an intricate field that intertwines with various aspects of Earth and planetary sciences, aiding in our effort to understand our planet and beyond.
Alert Levels: Volcanic Signals
Alert levels serve as a crucial system in predicting and understanding volcanic activity, thereby providing necessary warnings and guidelines for human safety. Volcanic signals are a specialized area of geophysics that studies these natural phenomena. Primarily, these signals are monitored through seismic activity, ground deformation, gas emissions, and other geophysical and geochemical measurements, which all contribute to determining the alert level of a volcano.
The alert levels typically range from normal, advisory, watch to warning, each indicating the escalating potential of a volcanic eruption. Normal signifies a dormant or non-active state, whereas advisory represents an increase in activity but without any imminent eruption. The watch level indicates heightened or escalating unrest with increased potential of eruption, while warning means hazardous activity is imminent, underway, or suspected.
These alert levels are paramount for local communities, emergency services, and public health officials. By monitoring the changes in a volcano’s behavior, they can prepare accordingly for any potential hazards. For instance, an increase in seismic activity or ground deformation can prompt officials to raise the alert level and advise the public to evacuate or take necessary precautions.
Volcanologists, scientists who study volcanoes and related phenomena, use various tools and techniques to monitor these signals. They include seismographs for detecting earthquake activity, ground-based radar for tracking ground deformation, and spectrometers for analyzing gas emissions. Data from these tools, combined with visual observations, help in identifying patterns and changes that precede volcanic eruptions.
In essence, alert levels and volcanic signals are integral elements in volcanic hazard management. They help in predicting potential eruptions and implementing appropriate mitigating measures, thus reducing risks and protecting lives and property. As technology continues to advance, so too does our ability to interpret these signals and refine the alert level system, making it an ever-evolving field of study.

Preparing for, During, and After an Eruption
Preparing for an eruption involves a series of steps to ensure safety and survival. First, it is essential to understand the risks associated with the specific volcano in question. This includes understanding the type of volcano, its eruption history, and its current activity. By far, the most critical preparation step is to have an evacuation plan in place, which should include knowing the safest escape routes and having a designated meeting place. In addition, individuals should have a disaster supply kit ready, filled with necessary items such as food, water, clothing, and medical supplies.
During an eruption, it is advised to stay calm and execute the prepared evacuation plan as quickly as possible. Following the instructions of local authorities is crucial to ensure safety. It is also important to wear long-sleeved shirts and long pants, goggles, and a mask to protect against falling ash. If home confinement is advised, seal windows and doors, turn off air conditioning units, and stay indoors to avoid inhaling ash.
After an eruption, people should continue adhering to instructions from local authorities and only return home when it is deemed safe. Cleaning up volcanic ash can be a hazardous task and should be done while wearing protective clothing and masks. Moreover, individuals should be aware of potential secondary hazards such as mudflows and landslides, which may occur after an eruption due to the altered landscape. Mental health is also an essential aspect to consider after an eruption. Surviving such a frightening event can take a toll on mental health, and it might be beneficial to seek professional help if the need arises. To sum up, preparation, swift action during an eruption, and careful post-eruption behavior can significantly increase the chances of survival and recovery.
Green Light: Standard Procedures
A green light in procedural terms often implies the granting of permission or the go-ahead to initiate or continue a process or activity. Standard procedures, on the other hand, are the established methods of carrying out tasks that are widely accepted within a community, organization, or industry. When the phrase ‘Green Light: Standard Procedures’ is used, it typically means that a certain procedure or action has been granted the permission to proceed as it complies with the standard practices or guidelines set by a regulating body or institution.
This could be in the context of a business deal, a scientific experiment, a construction project, or any other activity that requires adherence to certain norms or standards. The green light is a metaphorical representation of approval or sanction, while standard procedures refer to the accepted and recommended ways of doing things. It is crucial in any field to have a set of standard procedures to maintain quality, reliability, and consistency, and receiving a green light for these procedures signifies that they meet the required criteria or benchmarks.
However, it’s equally important to regularly review and update these procedures to ensure their relevance and effectiveness in changing contexts. Getting a green light for standard procedures can also serve as a confidence booster for those involved in the process, as it validates their actions and decisions. In summary, ‘Green Light: Standard Procedures’ could be seen as an affirmation of the adherence to recognized and accepted methods, paving the way for efficient and effective operations.
Yellow Light: Cautionary Measures
When it comes to navigating through traffic, understanding the significance of a yellow light is critical. The appearance of a yellow light at a traffic signal is a universal sign to prepare to halt your vehicle, as the light is about to transition to red. This is a cautionary measure that is intended to maintain the smooth flow of traffic and ensure the safety of all road users. It’s not merely a suggestion, but a fundamental rule of the road that every driver is expected to adhere to.
The yellow light serves as an intermediary phase between the green and red lights, providing drivers with the time they need to respond appropriately to the changing traffic conditions. When a driver sees the yellow light, they should reduce their speed and prepare to stop before the intersection. However, if a vehicle is too close to the intersection when the light changes from green to yellow, it may be safer for the driver to continue at the same speed rather than attempting to stop abruptly.
It’s crucial to remember that the yellow light isn’t an invitation to accelerate in an attempt to beat the red light. Such behavior can lead to dangerous situations, as other road users might not anticipate a vehicle rushing through a yellow or red light. This can result in collisions with vehicles that are following the rules and preparing to enter the intersection when their light turns green.
In conclusion, the yellow light is an essential component of traffic management systems, designed to promote safety by controlling the flow of traffic. It’s a cautionary measure that maintains order and prevents accidents. Therefore, every driver should respect the yellow light and respond appropriately, ensuring not only their safety but also that of others on the road.
Red Light: Emergency Protocols
Red light: Emergency Protocols are essential guidelines implemented in various sectors like healthcare, law enforcement, and transportation to ensure the safety and welfare of the public. When a red light is illuminated, it signifies an imminent emergency or danger, necessitating immediate attention and action from the relevant authorities. The protocols associated with the red light vary depending on the context. For instance, in medicine, it could indicate a critical patient needing immediate attention, while in transportation, it could mean a severe traffic condition or an obstruction on the road. Regardless of the context, the primary objective is to prevent any further escalation of the situation and ensure swift and efficient management of the crisis at hand.
These protocols are designed to be clear and straightforward, enabling all involved parties to understand their roles and responsibilities during an emergency. Training is often provided to ensure that everyone can respond effectively to a red light situation. The protocols include a series of steps to be followed, often in a specified order, to manage the situation effectively. For instance, the first step might involve notifying the appropriate personnel or emergency services, followed by taking the necessary action to mitigate the emergency.
The implementation and adherence to these protocols can often mean the difference between life and death. Hence, they are taken very seriously and are strictly enforced. Non-compliance with these protocols can lead to severe consequences, including penalties and disciplinary action. However, the primary focus is not on punishment but on education and prevention. These protocols are continually reviewed and updated based on new information, technology, and feedback from those on the ground. In this way, they remain relevant and effective in addressing the various emergencies associated with a red light situation.

Handling Ashfall: Guidelines
Handling ashfall is an essential skill especially for individuals living around active volcanoes. When a volcanic eruption occurs, it usually disperses volcanic ash into the atmosphere which eventually falls back to the ground. This ash can pose severe health risks and damage properties. Therefore, understanding how to deal with it is crucial. Here are few guidelines to follow.
Firstly, stay informed. Rely on trusted sources of information such as local authorities for updates and instructions. In case of an imminent ashfall, stay indoors as much as possible to reduce exposure. If it is necessary to go outside, use protective gear like masks and goggles to protect your eyes and lungs from ash particles.
Secondly, prepare your home. Close all windows, doors, and ventilation openings to prevent ash from getting inside. Cover machinery, water supplies and electronic equipment. If ash enters your home, clean it up promptly to avoid damage. When cleaning, dampen the ash with water to avoid stirring it up and causing respiratory problems.
Thirdly, use caution when driving. Volcanic ash can cause poor visibility and slippery conditions. If possible, avoid driving in these conditions. If you must drive, use your headlights and keep a safe distance from other vehicles.
Lastly, take care of your health. If you have respiratory conditions like asthma or bronchitis, avoid exposure to volcanic ash as it can exacerbate these conditions. Maintain a stock of necessary medications and seek medical attention if necessary.
Remember, handling ashfall effectively requires preparation, caution, and adherence to official advice. While these guidelines can help, they are not exhaustive. Always stay updated with information from local authorities and act accordingly to safeguard yourself and your property.
